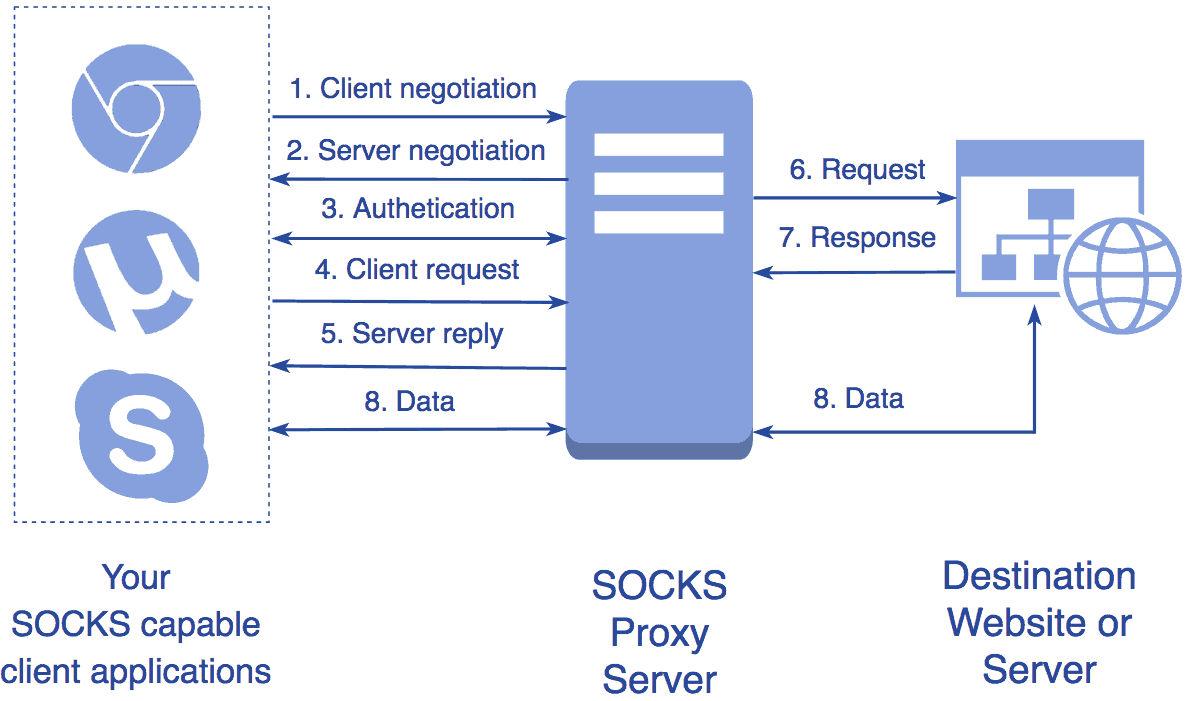
A socks server is an open source program/software that enables clients to access their own network and pass password protected information between them. Socks is an Internet Protocol that exchanges data packets between a server and client through a TCP server. There are some Socks used by free systems like socks-r, socks-ip and socks-lg. Socks offers authentication and encryption services, which are usually passed on by default.
An example of a socks server is Tcproxy. It is free software and is used as an SNTP proxy. Tcproxy can be configured with different settings. It accepts TCP/IP packets with the IP header or it can return the ICMP destination unreachable packets. The returned octets are then sent to the client IP address.
There are many common IP addresses that a socks server will accept. These are ‘inetwork IP’, ‘local IP address’ and ‘wan IP address’. For instance, if the local IP address is 10.1.1.x’, the returned octet for the packet will be ‘ 010’. If the local IP address is ‘ 10.1.x’ but the destination IP address is ‘lan’. Then the returned octet will be ‘001’. socks version 5 march | x’01 | ip address} The latest version of the Simple Network Management Protocol is RCPP and it is backwards compatible with older versions. The latest revision of RCPP is STD compliant. The latest draft of RCPP is in draft form with the latest changes being announced at PRI conferences. It is expected to undergo several reviews before becoming Final. Therefore, it is recommended to refer to the latest version for information on the latest developments on the sock server technology.